Why Everyone Should Try Intermittent Fasting: 7 Surprising Benefits
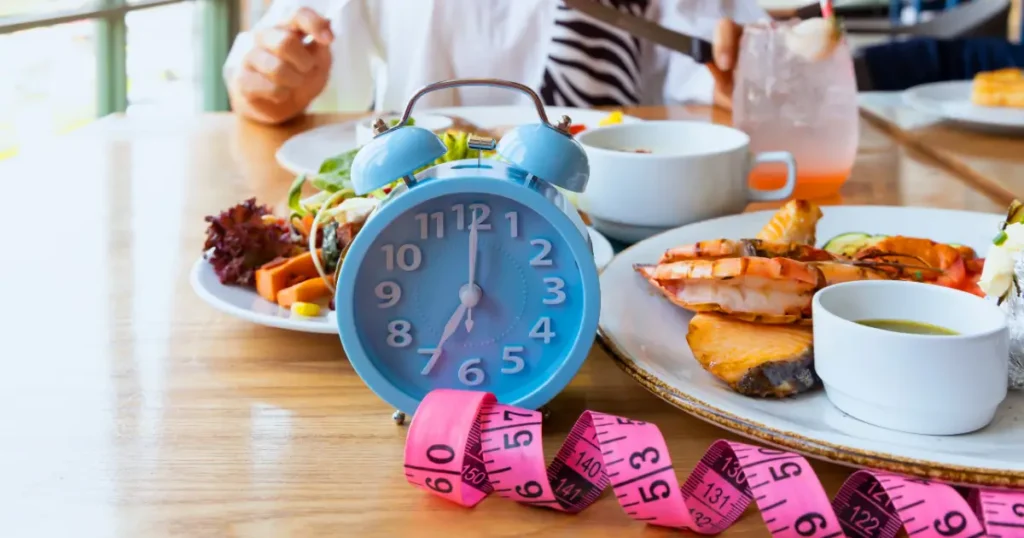

Imagine discovering that the idea of “breakfast as the most important meal of the day” is a myth crafted by the food industry to boost profits. We’ve been led to believe that constant eating is essential for health, especially to keep blood sugars stable. This narrative encourages eating breakfast, lunch, dinner, and snacks, leading to disrupted metabolic processes and issues like obesity, insulin resistance, and chronic inflammation.
Intermittent fasting, however, offers a different approach that aligns with our natural rhythms. By giving the body necessary breaks from food, it triggers autophagy—a process where cells cleanse and repair themselves—promoting fat burning and improved overall health.
Here are seven compelling reasons why intermittent fasting can transform your health and debunk the myth that constant eating is essential for maintaining blood sugar stability.
What is Intermittent Fasting?
Intermittent fasting involves cycling between periods of eating and fasting. The primary rule is to schedule specific times for eating and fasting. Popular methods include the 16/8 method (fast for 16 hours, eat for 8), the 5:2 diet (eat normally for five days, limit calories for two days), and the eat-stop-eat method (24-hour fast once or twice a week). During fasting periods, consume only non-caloric beverages like water, tea, or coffee. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any fasting regimen.
1. Weight Loss and Fat Burning

Weight loss and fat burning are central goals for many pursuing a healthier lifestyle. Intermittent fasting (IF) has emerged as a highly effective method for achieving these goals. By structuring periods of eating and fasting, intermittent fasting enhances the body’s natural ability to shed excess weight and burn fat, optimizing metabolic processes that have been honed through human evolution.
When we eat, our bodies utilize glucose from carbohydrates as the primary energy source. This glucose is stored in the liver and muscles as glycogen. During fasting, once glycogen stores are depleted, the body switches to burning fat for energy. This metabolic switch is crucial for fat loss. Research indicates that intermittent fasting boosts levels of norepinephrine, a hormone that facilitates fat breakdown and increases resting energy expenditure. This process, coupled with reduced insulin levels during fasting, accelerates fat burning.
Intermittent fasting also triggers a process called autophagy, where the body cleans out damaged cells and regenerates new ones, further promoting fat loss and overall health. Studies have shown that intermittent fasting can significantly reduce body weight and improve metabolic health by lowering insulin resistance and reducing inflammation. By adopting intermittent fasting, individuals can tap into these powerful physiological processes, achieving sustainable weight loss and enhanced fat burning, leading to a healthier, leaner body.
2. Improved Heart Health

Improved heart health is a significant benefit of intermittent fasting, contributing to the growing popularity of this eating pattern. Intermittent fasting positively influences several risk factors associated with cardiovascular disease, making it a powerful tool for maintaining a healthy heart. By alternating periods of eating and fasting, individuals can optimize their heart health through various physiological changes that occur during fasting.
One of the key ways intermittent fasting improves heart health is by reducing blood pressure. Studies have shown that fasting can lead to significant reductions in both systolic and diastolic blood pressure, which are critical for preventing heart disease. Additionally, intermittent fasting helps lower levels of LDL cholesterol (the “bad” cholesterol) and triglycerides, both of which are associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease. By improving lipid profiles, intermittent fasting supports better heart health and reduces the risk of atherosclerosis, a condition characterized by the buildup of fats and cholesterol in the artery walls.
Intermittent fasting also enhances insulin sensitivity, which plays a crucial role in heart health. Improved insulin sensitivity helps regulate blood sugar levels and reduce inflammation, both of which are linked to cardiovascular disease. Chronic inflammation is a known contributor to heart disease, and intermittent fasting has been shown to decrease inflammatory markers in the body. By reducing inflammation and improving metabolic health, intermittent fasting provides comprehensive benefits for heart health, making it an effective strategy for those looking to enhance their cardiovascular well-being.
3. Enhanced Cognitive Function

Enhanced cognitive function is one of the compelling benefits of intermittent fasting, making it a valuable practice for maintaining mental acuity and overall brain health. Intermittent fasting promotes neuroplasticity, the brain’s ability to adapt and reorganize itself by forming new neural connections. This process is essential for learning, memory, and cognitive resilience.
Research indicates that intermittent fasting can boost levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a protein that supports the survival of existing neurons and encourages the growth of new neurons and synapses. Increased BDNF levels are associated with improved memory, learning, and cognitive function. Additionally, intermittent fasting enhances mitochondrial function and stimulates autophagy in brain cells, processes that are crucial for clearing out damaged cells and improving cellular health, which helps protect against neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
Moreover, intermittent fasting can reduce oxidative stress and inflammation, both of which are detrimental to cognitive health. By lowering levels of inflammation and oxidative damage, intermittent fasting helps preserve brain function and prevent cognitive decline. Studies have shown that intermittent fasting can improve mental clarity, focus, and overall cognitive performance, making it a powerful tool for enhancing brain health and function throughout life.
4. Reduced Risk of Type 2 Diabetes

Reduced risk of type 2 diabetes is a significant benefit of intermittent fasting, largely due to its positive effects on insulin sensitivity. Insulin resistance, a condition where cells in the body become less responsive to insulin, is a primary factor in the development of type 2 diabetes. Intermittent fasting helps mitigate this condition by improving how the body processes insulin and regulates blood sugar levels.
When we eat frequently, our bodies are constantly producing insulin to manage blood glucose levels. Over time, this can lead to insulin resistance, where the body’s cells no longer respond effectively to insulin. Intermittent fasting, by contrast, reduces the frequency of insulin spikes, giving the body time to reset and improve insulin sensitivity. Research indicates that intermittent fasting can lower fasting insulin levels and reduce insulin resistance, making it easier for the body to manage blood sugar levels efficiently.
Furthermore, intermittent fasting aids in weight loss and reduces body fat, both of which are critical factors in managing and preventing type 2 diabetes. Excess body fat, particularly around the abdomen, is closely linked to insulin resistance. By promoting fat loss, intermittent fasting helps decrease the amount of fat in the liver and pancreas, improving these organs’ ability to regulate blood sugar. This comprehensive approach to improving insulin sensitivity and reducing body fat makes intermittent fasting a powerful strategy for lowering the risk of type 2 diabetes and enhancing overall metabolic health.
5. Anti-Inflammatory Effects

Intermittent fasting offers notable anti-inflammatory effects, which play a crucial role in enhancing overall health and preventing chronic diseases. Inflammation is the body’s natural response to injury or infection, but chronic inflammation can lead to a host of health issues, including heart disease, diabetes, and autoimmune disorders. Intermittent fasting helps reduce inflammation by promoting beneficial changes at the cellular and molecular levels.
One of the primary ways intermittent fasting reduces inflammation is by decreasing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, which are proteins involved in the inflammatory response. Studies have shown that intermittent fasting can lower levels of these cytokines, thereby reducing inflammation throughout the body. Additionally, fasting promotes autophagy, a process where the body cleans out damaged cells and regenerates new ones. This cellular cleanup helps reduce oxidative stress and inflammation, contributing to improved cellular health and function.
Moreover, intermittent fasting enhances gut health, which is closely linked to inflammation. A healthy gut microbiome is essential for maintaining the balance of pro- and anti-inflammatory signals in the body. Intermittent fasting can improve gut microbiota composition, promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria and reducing harmful bacteria that can trigger inflammation. By supporting a healthy gut and reducing systemic inflammation, intermittent fasting offers comprehensive benefits that contribute to better overall health and reduced risk of inflammatory diseases.
6. Autophagy and Cellular Repair

Intermittent fasting significantly enhances autophagy and cellular repair, processes vital for maintaining optimal health and preventing diseases. Autophagy, derived from the Greek words “auto” (self) and “phagy” (eating), is the body’s way of cleaning out damaged cells and regenerating new ones. This cellular recycling is crucial for removing dysfunctional components, thus preventing various diseases, including cancer and neurodegenerative disorders.
During periods of fasting, the body shifts its focus from growth and reproduction to maintenance and repair. This shift triggers autophagy, which helps remove damaged proteins and organelles, effectively rejuvenating cells. Research indicates that autophagy is essential for brain health, as it clears out protein aggregates and damaged mitochondria, thereby reducing the risk of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. Furthermore, autophagy supports the immune system by eliminating intracellular pathogens, contributing to enhanced immune function.
Intermittent fasting not only promotes autophagy but also improves overall cellular repair mechanisms. Fasting periods stimulate the production of growth factors that enhance tissue repair and regeneration. This process is particularly beneficial for the liver, muscle tissue, and the cardiovascular system. By facilitating the removal of cellular debris and promoting the regeneration of healthy cells, intermittent fasting aids in maintaining cellular integrity and function, leading to improved health and longevity. These profound effects on autophagy and cellular repair highlight intermittent fasting as a powerful tool for enhancing cellular health and preventing age-related diseases.
7. Longevity and Disease Prevention

Intermittent fasting has profound effects on longevity and disease prevention, making it a promising approach for enhancing long-term health. This practice influences various biological processes that contribute to aging and the development of chronic illnesses, positioning it as a powerful tool for extending lifespan. One of the primary ways intermittent fasting promotes longevity is by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation, which are closely linked to aging and chronic diseases. During fasting, the body lowers the production of free radicals and enhances its antioxidant defenses, protecting cells from damage and promoting healthier aging.
Additionally, intermittent fasting triggers autophagy, a cellular cleanup process where the body removes damaged cells and regenerates new ones. This mechanism is crucial for preventing age-related diseases such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and certain cancers. By regularly engaging in fasting, the body maintains a more efficient system for cellular repair and regeneration, contributing to improved overall health and longevity. Autophagy not only helps in detoxifying cells but also supports the immune system by eliminating intracellular pathogens, thereby reducing the risk of infections and inflammation-related diseases.
Moreover, intermittent fasting significantly improves metabolic health by enhancing insulin sensitivity and reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes, obesity, and cardiovascular diseases. Improved insulin sensitivity helps regulate blood sugar levels and prevent metabolic dysfunctions associated with aging. Studies have shown that intermittent fasting can also improve heart health by lowering blood pressure, reducing LDL cholesterol levels, and decreasing triglycerides, all of which are critical risk factors for cardiovascular diseases. By influencing these vital health markers, intermittent fasting offers a comprehensive strategy for disease prevention and longevity, supporting a healthier and more resilient body as it ages.
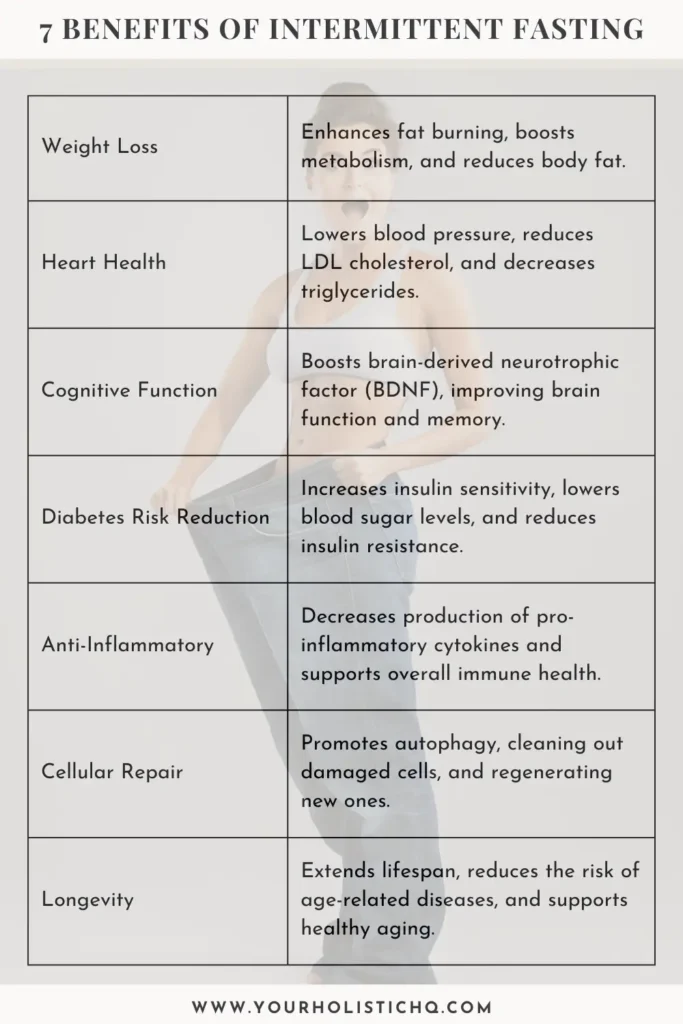
Benefits of Intermittent Fasting
| Weight Loss and Fat Burning | Intermittent fasting enhances the body’s ability to burn fat and reduces insulin resistance, leading to significant weight loss and improved metabolic health. |
| Improved Heart Health | Fasting helps lower blood pressure, reduce LDL cholesterol levels, and decrease triglycerides, thereby reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease. |
| Enhanced Cognitive Function | Intermittent fasting boosts levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), improving memory, learning, and overall cognitive function while reducing oxidative stress and inflammation. |
| Reduced Risk of Type 2 Diabetes | By improving insulin sensitivity and lowering fasting insulin levels, intermittent fasting reduces the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. |
| Anti-Inflammatory Effects | Intermittent fasting decreases the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and improves gut health, thereby reducing systemic inflammation and the risk of chronic diseases. |
| Autophagy and Cellular Repair | Fasting triggers autophagy, a process that removes damaged cells and regenerates new ones, supporting cellular health and longevity. |
| Longevity and Disease Prevention | Intermittent fasting reduces oxidative stress, enhances metabolic health, and promotes cellular repair, all of which contribute to a longer lifespan and reduced risk of chronic diseases. |
Final Thoughts

Intermittent fasting transcends being merely a dietary trend; it embodies a holistic and scientifically validated approach to enhancing overall health, cognitive function, and longevity. By embracing intermittent fasting, individuals can harness a multitude of benefits beyond mere weight loss. These include significant reductions in inflammation, improved heart health, enhanced insulin sensitivity, and the promotion of cellular repair through autophagy. Each of these benefits plays a critical role in preventing chronic diseases and fostering a healthier, longer life.
This practice taps into our natural biological rhythms, providing a sustainable method for weight management and metabolic health improvement. Intermittent fasting encourages the body to function more efficiently, optimizing energy use and cellular maintenance by allowing necessary breaks from constant food intake. The profound impact of intermittent fasting on insulin resistance, inflammation, and cardiovascular health makes it an invaluable tool for those seeking to enhance their health span and life span.
Imagine if everyone adopted this powerful practice—who would be most affected? The pharmaceutical industry, of course. The widespread adoption of intermittent fasting could dramatically reduce the incidence of chronic diseases such as type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular conditions, and neurodegenerative disorders, thereby diminishing the need for numerous medications. Knowledge is indeed power. By understanding and leveraging the benefits of intermittent fasting, individuals can take control of their health, reduce reliance on pharmaceutical interventions, and achieve a higher quality of life. In sum, intermittent fasting offers a versatile and effective solution for those seeking to improve their overall well-being and longevity.